Mushrooms are a type of fungus, and while they are not plants, they are also not animals. Fungi are a distinct kingdom, separate from animals and plants, and are more closely related to animals than plants. They do not photosynthesize like plants, nor do they ingest their food like animals. Instead, they live inside their food and secrete enzymes to dissolve nutrients, which they then absorb.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of organism | Fungi |
| Feeding method | Secrete enzymes to dissolve nutrients and then absorb them |
| Relationship to animals | More closely related to animals than plants |
| Relationship to plants | Historically grouped with plants |
| Number of species | Approximately 14,000 |
| Identification | Standard methods include examination of juices, bruising reactions, odors, tastes, shades of color, habitat, habit, and season |
| Alternative uses | Mycelium is an alternative to animal leather and plastic packaging |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Mushrooms are a type of fungus
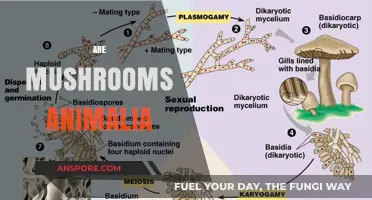
The term "mushroom" is used to describe the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota. The gills of the mushroom produce microscopic spores, which help the fungus spread across the ground or its occupant surface. These spores are called basidiospores and are produced on the gills, falling in a fine rain of powder from under the caps. At the microscopic level, the basidiospores are shot off basidia and then fall between the gills in the dead air space.
The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. The word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi that have a stem (stipe), a cap (pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) on the underside of the cap. "Mushroom" also describes a variety of other gilled fungi, with or without stems. Forms deviating from the standard morphology usually have more specific names, such as "bolete", "truffle", "puffball", "stinkhorn", and "morel".
Mushrooms develop from a nodule or pinhead, less than two millimeters in diameter, called a primordium, which is typically found on or near the surface of the substrate. It is formed within the mycelium, the mass of thread-like hyphae that make up the fungus. The primordium enlarges into a roundish structure of interwoven hyphae, resembling an egg, called a "button". The button has a cottony roll of mycelium, the universal veil, that surrounds the developing fruit body. As the egg expands, the universal veil ruptures and may remain as a cup, or volva, at the base of the stalk, or as warts or volval patches on the cap.
Fungi, including mushrooms, play vitally important roles in nature and to humans. They are responsible for keeping us from drowning in a sea of leaf litter and fallen sticks and branches. They also create antibiotics and other drugs.
Mushrooms and Pectin: A Natural Pairing?
You may want to see also

Fungi are more closely related to animals than plants
Mushrooms are a kind of fungus. Fungi have historically been grouped with plants, but this classification is incorrect. Fungi are more closely related to animals than plants. This conclusion is supported by the best available molecular evidence, which provides robust evolutionary histories that indicate organismal relationships and estimate divergence times from common ancestors.
Fungi do not photosynthesize like plants, nor do they ingest their food like animals. Instead, they live inside their food and secrete enzymes to dissolve nutrients, which they then absorb. This unique feeding mechanism is one of the reasons why fungi are considered distinct from plants and animals.
Fungi share a common ancestor with animals in the form of an opisthokont, a cell with a posterior flagellum, similar to human spermatozoids. This evolutionary relationship has been uncovered through molecular approaches that have revolutionized our understanding of life. Fungi, bacteria, archaea, and eukarya are now recognized as four possible major domains of life, distinguished by their cellular components and cell membrane composition.
While the study of fungi (mycology) has traditionally been a botanical pursuit, it is distinct from plant science. Fungi have their own kingdom, which includes yeasts, molds, mushrooms, wood-ears or conks, and several other types of unicellular and multicellular organisms. This kingdom is incredibly diverse, with estimates suggesting that we have only discovered 10% of the species within it.
The unique characteristics of fungi have important implications for various industries. For example, mycelium, a group of mostly invisible fungi including mushrooms, can be used as an alternative to animal leather and plastic packaging, offering more sustainable options for the fashion industry. Additionally, the study of fungi can provide valuable insights into evolution, ecology, and cellular biology, highlighting the importance of recognizing their distinct classification from plants and animals.
Mushrooms: Nature's Wake-Up Call or Sleepytime Tea?
You may want to see also

Fungi are not plants
Mushrooms are a type of fungus. Fungi are not plants, though they may look similar. Fungi have a different method of feeding than plants. They excrete digestive enzymes into their environment and absorb nutrients from it. They do not make their own food from sunlight, like plants do. Fungi are also unable to move to find food sources, unlike animals.
Fungi are classified separately from plants because their cells are structured differently and they have distinct genetic lineages. Plants have cell walls made of cellulose, while fungi have cell walls made of chitin. Plants store food as starches, whereas fungi store food as glycogen, like animals. Fungi also do not contain chloroplasts, which are structures that plants and some other organisms use for terpene biosynthesis.
Fungi are important decomposers of organic matter and play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and exchange in the environment. They are often found in soil or on dead matter, where they help break down leaves, plants, and other organic material. They also form symbiotic relationships with plants, helping trees absorb nutrients and water from the soil.
While fungi share some similarities with both plants and animals, their unique cellular structure, genetic lineage, and feeding methods set them apart. They are classified as their own kingdom, separate from plants, animals, and bacteria.
Mushrooms: Starchy or Not?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Fungi do not photosynthesize or ingest food
Mushrooms are a kind of fungus. Fungi are not plants, despite having been grouped with plants historically. They are also not animals. Fungi have their own kingdom, separate from plants, animals, and bacteria.
Fungi do not photosynthesize. They do not make their own food through photosynthesis by absorbing nutrients. Instead, they obtain nutrients by absorbing them from their environment after breaking them down externally using enzymes. This process involves the release of exoenzymes and the absorption of simpler molecules through mycelium. Mycelium is the branching network of fine filaments (hyphae) that make up the body of a fungus. Fungi are classified as heterotrophs, which means they obtain organic compounds from their environment, rather than producing their own food.
This process of external digestion can be broken down into four steps. First, fungi release special enzymes known as exoenzymes into their surrounding environment. These enzymes break down complex organic materials into smaller, absorbable molecules. Second, the resulting simpler molecules are then absorbed through structures called mycelia. Third, the fungi grow. Unlike animals, growth is the means of mobility for fungi, except for spores, which may travel through the air or water. Finally, some fungi form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic organisms. Lichens, for example, are a symbiotic relationship between fungi and photosynthetic algae or cyanobacteria.
Fungi are unique organisms that play an important ecological role as decomposers. They break down dead things like leaves and plants. This is why mushrooms, which are the fruiting bodies of fungi, are often seen growing on dead trees or logs.
LED Lights: Do They Harm Mushrooms?
You may want to see also

Fungi are decomposers
Mushrooms are a type of fungus. Fungi are not animals; they are part of the kingdom Fungi, which includes microorganisms such as yeasts and moulds, as well as mushrooms. Fungi are distinct from plants and animals in that they lack chlorophyll, the pigment that allows plants to make their own food using sunlight. Instead, fungi are decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter and returning vital nutrients to the environment.
Fungi play a critical role in the ecosystem as decomposers, breaking down complex organic materials into simpler inorganic substances. They secrete enzymes that can break down large, complex molecules like carbohydrates and proteins into simpler components, releasing energy in the process. This process makes essential nutrients available to primary producers, usually plants and algae, which can then be used to grow and reproduce.
Fungi obtain their nutrients from the dead organic matter that they break down. They are often found growing on dead trees or logs, feeding on the decaying wood. Some types of fungi, such as shelf fungi, can even parasitize living trees, causing their eventual death. Fungi are also responsible for breaking down dead animals, returning important elements like nitrogen and phosphorus to the environment, which would otherwise remain trapped in decaying matter.
The role of fungi as decomposers is vital to the survival of many other organisms. Without the activity of fungi and their bacterial allies, essential nutrients from dead animals and plants would be unavailable for use by other organisms. Fungi are particularly important decomposers in forest ecosystems, where they help to recycle nutrients and maintain the health of the forest.
In addition to their ecological importance, fungi also have practical applications for humans. Some types of mushrooms are edible and can be delicious food sources. Fungi also play a role in the creation of certain foods and drinks, such as cheese and alcohol, through the process of fermentation. Understanding the role of fungi as decomposers can help us appreciate their value and importance in the natural world and our daily lives.
Mushrooms: Nature's Source of Vitamin D
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, mushrooms are not animals. They are fungi, which are part of a separate kingdom from Animalia and Plantae. Fungi are more closely related to animals than plants, but they are not animals. Fungi are microorganisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms.
Structurally, mushrooms are more similar to plants than animals as they have rigid cell walls made from long-chain polysaccharides, or sugars. However, in a metabolic sense, mushrooms are more similar to humans than plants as they take in oxygen and give off carbon dioxide, meaning they breathe like humans.
Mushrooms and animals are both heterotrophs, meaning they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment.