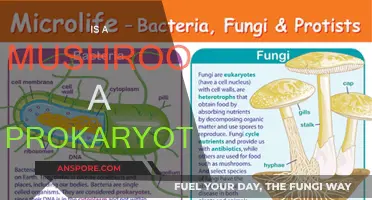
Mushrooms are a type of fungus, typically produced above ground on soil or another food source. They are characterised by a stem, a cap, and gills on the underside of the cap. Mushrooms are often classified as decomposers because they break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. They secrete enzymes that help them absorb nutrients from decaying organisms. This process is essential for maintaining a healthy ecological balance. However, some sources classify mushrooms as consumers because they obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter. In contrast, producers, such as plants, create their own food through photosynthesis and are essential for energy flow in an ecosystem.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of organism | Fungi |
| Ecological role | Decomposer |
| Food source | Dead organic matter |
| Food production | No |
| Photosynthesis | No |
| Nutrient source | Absorbed from decomposed organisms |
| Nutrient cycling | Yes |
| Enzymes | Yes |
| Vitamin D content | Yes |
Explore related products
$14.99
What You'll Learn

Mushrooms are decomposers
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that breaks down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, into simpler substances. They are classified as decomposers as they secrete enzymes that help them decompose and absorb nutrients from decaying organisms. This process is essential for recycling nutrients in ecosystems.
Mushrooms, like all fungi, play a vital role in maintaining a healthy ecosystem. They absorb nutrients from dead organic material, helping to sustain plant life. They are not producers, as they do not create their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter.
A common example of mushrooms as decomposers is their growth on rotting logs. As they decompose the wood, they release nutrients back into the soil, benefiting the surrounding plant life. This enhances soil fertility and ensures a healthy balance in the environment, allowing various species to thrive.
The role of mushrooms in breaking down organic material has been well-documented. They are known to secrete enzymes that help decompose and absorb nutrients from decaying organisms. This process involves converting complex organic substances into simpler compounds that they can absorb. Mushrooms break down tough components like cellulose and lignin, which are found in wood and plant tissues.
In summary, mushrooms are considered decomposers as they break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. They play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and enhancing soil fertility.
Mushroom Coffee Halal Status: What Muslims Should Know
You may want to see also

They break down dead organic matter
Mushrooms are considered fungi, which means they break down dead organic matter into simpler substances. They are classified as decomposers because they break down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, and absorb nutrients from decaying organisms. Mushrooms secrete enzymes that help them decompose and absorb nutrients from an organism. This process is essential for recycling nutrients in ecosystems.
Mushrooms play a vital role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil. They grow on rotting logs and, as they decompose the wood, they release nutrients back into the soil, benefiting surrounding plant life. This process of breaking down organic material enhances soil fertility.
Mushrooms are not producers because they do not create their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they are consumers because they obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter. They are also considered decomposers because they break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients.
Scientific studies show that fungi, including mushrooms, are critical for nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Their role in breaking down organic material has been well-documented, and they are essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Psychedelic Visions: Exploring Mushroom Trips
You may want to see also

They recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem
Mushrooms are not producers, but they are vital to the ecosystem. They are part of the fungi kingdom and are considered decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process of decomposition is essential for maintaining a healthy balance in the environment, allowing various species to thrive.
Mushrooms secrete enzymes that help them decompose and absorb nutrients from decaying organisms. They break down tough components like cellulose and lignin, found in wood and plant tissues. As they decompose the wood, they release nutrients back into the soil, benefiting surrounding plant life. This enhances soil fertility and ensures a healthy ecological balance.
Fungi, including mushrooms, are critical for nutrient cycling in ecosystems. They play an essential role in breaking down organic material and converting complex organic substances into simpler compounds that they can absorb. This process of converting complex substances into simpler ones is a key function of decomposers, allowing them to recycle nutrients effectively.
Mushrooms, as decomposers, feed on dead organisms and waste materials. They are consumers that obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter. In contrast, producers, such as plants, create their own food through photosynthesis. They take in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen, providing the basis for most other organisms' sustenance.
Dehydrating Oyster Mushrooms: A Smart Preservation Method
You may want to see also
Explore related products

They are part of the fungi kingdom
Mushrooms are part of the fungi kingdom, which means they are decomposers. They break down dead organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process is known as decomposition, and it is vital for maintaining a healthy ecological balance. Mushrooms play a crucial role in this process by breaking down complex organic substances into simpler compounds that can be absorbed by other organisms.
Mushrooms are not producers, as they do not create their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter. They secrete enzymes that help them decompose and absorb nutrients from decaying organisms, such as plants and animals. This process of nutrient cycling is essential for ecosystems, as it ensures a healthy balance in the environment, allowing various species to thrive.
Fungi, including mushrooms, have a unique structure that facilitates their role as decomposers. They produce microscopic spores, which help them spread and colonize new areas. These spores are typically found on the gills of mushrooms, and they play a crucial role in the reproduction and dispersal of fungi. The gills produce a fine rain of powder, known as basidiospores, which contribute to the decomposition process.
Mushrooms are often classified based on their macroscopic structure, such as the presence or absence of stems, caps, and gills. However, identification to the species level requires a more detailed understanding of their microscopic characteristics. Additionally, mushrooms are known to have important nutritional benefits, such as providing vitamin D when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, either naturally or through artificial means.
In summary, mushrooms are part of the fungi kingdom and play a vital role as decomposers in ecosystems. They break down organic matter, recycle nutrients, and contribute to the overall ecological balance. While mushrooms are not producers, their ability to decompose and recycle nutrients makes them essential for the health and sustainability of various ecosystems.
Mushroom Hunting: Best Places for Murals
You may want to see also

Mushrooms are not producers
Mushrooms are not capable of producing their own food through photosynthesis like producers such as plants and algae. Instead, they obtain their nutrients by breaking down organic matter. They release enzymes that help them decompose and absorb nutrients from dead organisms and waste materials. This process of breaking down dead organic matter is crucial for the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems.
A common mistake is to classify mushrooms as consumers or producers. However, they are distinct from both groups as they do not directly consume other organisms or produce their own food. Instead, they play a vital ecological role by breaking down and recycling organic matter, which provides sustenance for other organisms in the ecosystem.
While mushrooms may appear to be simple organisms, their identification to species can be challenging and often requires a detailed understanding of their macroscopic and microscopic structures. Their classification as decomposers highlights their unique ecological role and the importance of fungi in maintaining healthy ecosystems.
The Importance of Rinsing Shitake Mushrooms
You may want to see also