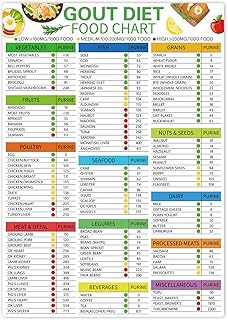
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by chronically elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which can be caused by unhealthy diets, such as high-purine diets. Purine intake is rarely the cause of gout, and it is typically caused by the body's inability to flush uric acid out. While mushrooms are not considered high in purines, they contain moderate amounts and are on the higher side for non-meat sources. For example, Shimeji and Shiitake mushrooms are considered to be on the lower end of the purine spectrum, whereas dried Shiitake mushrooms have a higher purine level by weight. Substituting meat with mushrooms can help lower purine intake, as mushrooms are lower in purines than meat and are also lower in calories and fat.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purine levels in mushrooms | Moderate, varies between types |
| Types of mushrooms with lower purine levels | Shimeji, shiitake |
| Gout | Caused by chronically elevated levels of uric acid in the diet |
| Gout prevention | Avoid red meat, beer, organ meats, high fructose products, and being overweight |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Purine levels in mushrooms vary by type
Purine levels in mushrooms vary depending on the type of mushroom. For example, Shimeji mushrooms are considered to be low in purines, whereas other types of mushrooms, such as shiitake, are moderate to high in purines, especially when dried.
Purines are naturally occurring substances found in many foods, including mushrooms. While mushrooms may not be the main cause of gout, a build-up of uric acid, which is a byproduct of purine metabolism, can lead to gout attacks. Gout is a form of arthritis caused by chronically elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, which can result from unhealthy diets, such as high-purine diets.
Some studies have found a link between mushroom consumption and hyperuricemia, which is a condition characterised by elevated uric acid levels in the blood. However, the results may vary depending on age and cultural dietary habits. For example, a study conducted among middle-aged and older Japanese men found an association between mushroom consumption and hyperuricemia. In contrast, a study conducted in China suggested a positive association between the risk of hyperuricemia and younger age.
It is important to note that while purine intake is important, it is not the only factor contributing to gout. Other factors include carrying excess weight, consuming high-fructose products, and drinking alcohol, especially beer, as it can prevent uric acid from leaving the body. Therefore, maintaining a healthy weight and making dietary substitutions, such as choosing mushrooms over red meat, can help manage gout and lower purine intake.
White Mushrooms: Natural Anti-Inflammatory Superheroes?
You may want to see also

Mushrooms are a healthier alternative to meat
Secondly, mushrooms can be a good substitute for meat in terms of purine levels. Purine intake is rarely the sole cause of gout, a form of arthritis caused by chronically elevated levels of uric acid in the diet. While some sources suggest that mushrooms are moderate in purines, others indicate that there is a range of purine levels across different types of mushrooms. For example, Shimeji mushrooms are considered to be quite low in purines, whereas dried Shiitake mushrooms are purported to have higher levels of purines. Therefore, substituting meat with specific types of mushrooms can help to reduce purine intake and lower the risk of gout.
Furthermore, research suggests that mushroom consumption is linked to a reduced risk of hyperuricemia, especially in older individuals. A study conducted in Japan found that the prevalence of hyperuricemia was significantly higher in individuals under 60 years of age compared to those aged 60 and above. This indicates that age may play a role in the relationship between mushroom consumption and hyperuricemia.
In conclusion, mushrooms are a healthier alternative to meat due to their weight management benefits and lower purine levels, specifically in certain varieties such as Shimeji mushrooms. Additionally, mushroom consumption may help to reduce the risk of hyperuricemia, especially in older adults. However, it is important to note that individual responses to mushroom consumption may vary, and further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between mushroom intake and health outcomes.
Swap Mushrooms for These Ingredients in Your Next Dish
You may want to see also

Gout is caused by elevated uric acid levels
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes inflammation and intense pain, typically in the toe joints, ankles, and knees. It is caused by elevated uric acid levels, which is known as hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia is usually diagnosed after gout or kidney stones cause symptoms.
Uric acid is a waste product in the body that is created when the body breaks down purines, which are chemical substances that occur naturally in the body and in some foods. Purines are not harmful in small amounts, but eating a diet high in purines can cause uric acid to build up in the blood over time. This can lead to gout, as the uric acid builds up in the joints and tissues, causing pain, swelling, and discoloration.
High-purine foods include red meat, shellfish, sweets, sugary sodas, and high-fructose corn syrup. Alcohol consumption also increases the risk of gout and gout flares, as it stops uric acid from leaving the body. Obesity and family history are other factors that can contribute to elevated uric acid levels and gout.
To prevent gout, it is recommended to follow a low-purine diet and maintain a healthy weight. Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water or mushroom-based dishes, can also help to dilute and flush out uric acid from the body.
Maitake Mushroom Wisdom: Who Owns the Company?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Alcohol consumption affects uric acid levels
Gout is a type of arthritis that commonly affects the feet and toes. It is caused by a build-up of uric acid in the body, which is a byproduct of chemical compounds called purines. Purines are found in certain foods, such as red meat and seafood, and in drinks, including alcohol. While purine-rich foods and drinks can contribute to elevated uric acid levels, other factors also play a role in the development of gout.
Alcohol consumption has been linked to increased uric acid levels in the blood, which can trigger gout attacks. Beer, in particular, has been identified as the alcoholic drink with the highest purine content and the strongest association with gout. One study found that men who drank one serving of beer daily had a 50% higher likelihood of developing gout, while those who drank two or more servings had 2.5 times the risk. However, it is important to note that other alcoholic beverages, such as wine and liquor, can also trigger gout symptoms in susceptible individuals.
The relationship between alcohol consumption and gout has been the subject of various studies. While some research suggests a connection between alcohol intake and elevated uric acid levels, a Mendelian randomization study found no causal link between predicted drinks consumed per week and gout risk or serum uric acid levels. This indicates that while alcohol may influence uric acid levels, other factors, such as genetic predisposition, also come into play.
It is worth noting that the impact of alcohol on uric acid levels and gout risk may vary across different populations. A study focusing on middle-aged and older Japanese men observed an association between mushroom consumption and hyperuricemia, with a higher prevalence of the condition in individuals under 60. Additionally, a study in China found a positive correlation between the risk of hyperuricemia and younger age, attributing this to unhealthy dietary habits and social activities involving heavy alcohol consumption.
Overall, while alcohol consumption may affect uric acid levels and contribute to the risk of gout, it is not the sole determinant. Genetic factors, dietary choices, and other lifestyle habits also play a role in the development of gout. For individuals with gout or those at risk, it is advisable to maintain a healthy weight, follow a balanced diet, and drink in moderation to minimize the likelihood of gout attacks.
Mellow Mushroom Alcohol Sales: What's Available?
You may want to see also

Exercise can help prevent gout flare-ups
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by a build-up of uric acid crystals in the joints. This can be due to the consumption of high levels of purines, or the body's inability to effectively remove the excess uric acid. While purine levels in mushrooms do not seem to be explicitly stated, substituting mushrooms for meat can lower purine intake. Additionally, mushrooms are a healthy weight-management option, which is beneficial as obesity increases uric acid levels.
Exercise can be an effective way to prevent gout flare-ups and manage the condition. During a gout flare-up, it is important to rest, apply ice, and elevate the affected area. However, maintaining a regular routine of low- to moderate-intensity exercises, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, between flare-ups can help reduce inflammation and uric acid levels. These exercises also aid in improving cardiovascular health, which is crucial for gout patients who are at higher risk of developing high blood pressure and coronary artery disease.
It is recommended to start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity to prevent excessive strain on the joints. Aquatic exercises, such as swimming or water aerobics, can be particularly beneficial due to the buoyancy of the water, which reduces the impact on the joints. Additionally, flexibility exercises like yoga can improve mobility.
It is important to consult a physician and physical therapist before starting an exercise routine to ensure a safe and effective program.
Gout flare-ups can be managed and prevented through a combination of rest, low-impact exercises, and gradual progression to higher-intensity activities. By taking a proactive approach to joint health, individuals with gout can maintain their mobility and flexibility while reducing the risk of future flare-ups.
Mushroom Identification: UK Foraging
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Mushrooms are not high in purines per se, but they contain moderate amounts and are on the higher side for non-meat sources. The purine level varies between different types of mushrooms. Shimeji mushrooms, for example, are considered to be quite low in purines, whereas dried shiitake mushrooms have a higher purine content.
Purine-rich foods can lead to elevated uric acid levels in the blood, which is a condition known as hyperuricemia. This, in turn, can cause gout, a form of arthritis where crystals of uric acid are deposited in different joints.
Gout attacks can be debilitating, but the condition is treatable with medical care and lifestyle changes. It is recommended to avoid foods that contribute to gout attacks, such as red meat, beer, organ meats, and high-fructose products. Losing weight, exercising, and increasing fluid intake to flush out uric acid can also help manage gout.
Yes, mushrooms can be a good alternative to meat if you are managing gout. Fresh mushrooms are low in fat and calories, and their high water content contributes to your daily fluid intake, helping to dilute and flush out uric acid. Substituting meat with mushrooms can lower your purine intake and improve weight management and heart health.