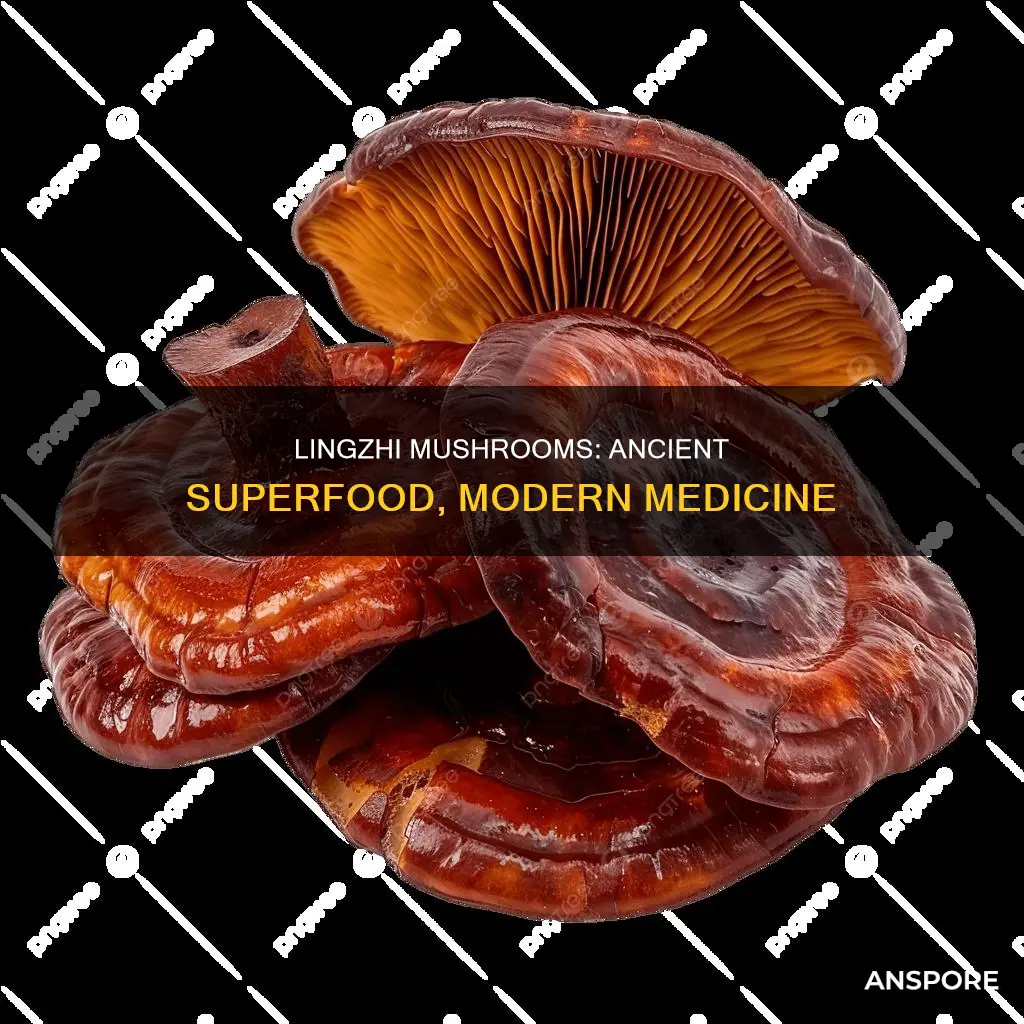
Lingzhi, also known as reishi, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in Asia. It is a large, dark mushroom with a glossy exterior and a woody texture. In Chinese, the name lingzhi means divine mushroom and represents a combination of spiritual potency and essence of immortality. It has been recognized as a medicinal mushroom for over 2,000 years and is used in traditional Chinese medicine. The lingzhi mushroom is unique in that its pharmaceutical rather than nutritional value is paramount. It has been reported to have various health benefits, including boosting the immune system, anti-inflammatory effects, and controlling blood glucose levels. However, its safety has recently been questioned.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Common name | Lingzhi, Reishi, Mannentake |
| Botanical name | Ganoderma lucidum, Ganoderma sichuanense, Ganoderma lingzhi |
| Appearance | Large, dark mushroom with a glossy exterior and woody texture |
| Cap width | 1-14 inches |
| Shape | Bracket fungus with a reddish-brown, shiny top |
| Growth | Parasite or saprotroph on deciduous trees, especially maples |
| Occurrence | East Asia, North America |
| Uses | Medicinal, nutritional supplements, tea |
| Benefits | Anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antiulcer, antitumorigenic, immunostimulating, immune system booster |
| Traditional beliefs | Symbol of success, well-being, divine power, and longevity |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Lingzhi is a medicinal mushroom with a long history of use in East Asian countries
- It is also known as Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, or mannentake
- It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antiulcer, antitumorigenic, and immunostimulating effects
- Lingzhi is rare in its natural form but can be cultivated on hardwood logs, sawdust, or woodchips
- Its name means mushroom of immortality in Chinese

Lingzhi is a medicinal mushroom with a long history of use in East Asian countries
Lingzhi, also known as reishi from its Japanese pronunciation, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in East Asia. It is a large, dark mushroom with a glossy exterior and a woody texture. The Latin word lucidus means "shiny" or "brilliant" and refers to the varnished appearance of the surface of the mushroom. In nature, it grows at the base and stumps of deciduous trees, especially maples.
Lingzhi has been recognized as a medicinal mushroom for over 2,000 years, with some evidence suggesting its use in Neolithic China 6,800 years ago. It is regarded as the "herb of spiritual potency" and is a symbol of success, well-being, divine power, and
The specific applications and attributed health benefits of lingzhi include control of blood glucose levels, modulation of the immune system, hepatoprotection, bacteriostasis, and more. Recent studies in the West have also shown that lingzhi stimulates the body's immune system. It can be ground or purchased commercially and steeped for tea. The flavor of the tea is strong and bitter, but it can be balanced with honey or sugar.
Various polysaccharides have been extracted from the fruit body, spores, and mycelia of lingzhi. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides (GL-PSs) are reported to exhibit a broad range of bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antiulcer, antitumorigenic, and immunostimulating effects. Polysaccharides are normally obtained from the mushroom by extraction with hot water followed by precipitation with ethanol or methanol, but they can also be extracted with water and alkali.
Portabella Mushrooms: Are They Fattening?
You may want to see also

It is also known as Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, or mannentake
The Lingzhi mushroom, also known as Ganoderma lucidum, Reishi, or mannentake, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in Asia. It is a large, dark mushroom with a glossy exterior and a woody texture. The Latin word "lucidus" means "shiny" or "brilliant" and refers to the varnished appearance of the surface of the mushroom. In China, it is called lingzhi, while in Japan, the name for the Ganodermataceae family is reishi or mannentake.
The name "lingzhi" in Chinese represents a combination of spiritual potency and the essence of immortality and is regarded as the "herb of spiritual potency," symbolizing success, well-being, divine power, and longevity. It is also known as the "mushroom of immortality" and has been revered for over 2,000 years, with some evidence suggesting use in Neolithic China 6,800 years ago. The proliferation of images of the Ganoderma lucidum mushroom began in 1400 AD and they are associated with Taoism, although they also extended beyond religion and appeared in various forms of art.
In nature, the lingzhi mushroom grows at the base and stumps of deciduous trees, especially maples. It is rare in its wild form, with only two or three out of 10,000 such trees exhibiting lingzhi growth. However, it can be effectively cultivated on hardwood logs, sawdust, or woodchips. The lingzhi mushroom is used in traditional Chinese medicine and has various potential health benefits, including boosting the immune system, controlling blood glucose levels, and exhibiting anti-inflammatory properties.
The scientific community has debated the appropriate scientific name for the lingzhi mushroom, with some arguing for Ganoderma sichuanense, while others prefer Ganoderma lingzhi. The former is the most widely found species in Chinese herb shops today, while the latter is considered the best fit for traditional definitions of the lingzhi mushroom. However, it is now established that Asian and European populations of Ganoderma lucidum are distinct from each other both morphologically and phylogenetically.
Mushrooms: Invasive or Not?
You may want to see also

It is believed to have anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antiulcer, antitumorigenic, and immunostimulating effects
The lingzhi mushroom, also known as Ganoderma lucidum, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in Asia. It has been recognised as a medicinal mushroom for over 2000 years, with powerful effects documented in ancient scripts. In Chinese, the name "lingzhi" represents a combination of spiritual potency and the essence of immortality.
Lingzhi mushrooms have a range of polysaccharides that are reported to exhibit several bioactivities. These include anti-inflammatory, hypoglycemic, antiulcer, antitumorigenic, and immunostimulating effects.
The anti-inflammatory effects of lingzhi mushrooms are believed to be due to their ability to alter inflammation pathways in white blood cells, specifically T lymphocyte cells (T cells). These white blood cells play a crucial role in immunity by fighting against infections and cancer. Research has also shown that lingzhi can affect the genes in these white blood cells.
Hypoglycemic actions of lingzhi mushrooms have been observed in studies on obese/diabetic mice. In these studies, water extracts of Ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies were found to have novel hypoglycemic effects.
Lingzhi mushrooms are also believed to have antitumorigenic properties. The chemopreventive activities of the mushroom on prostate cancer have been demonstrated, with one study showing that an extract of lingzhi suppressed the growth of prostate cancer cells. Another study found that lingzhi could inhibit the DNA damage response pathway and enhance the chemotherapy effect of carboplatin.
Lastly, lingzhi mushrooms are thought to have immunostimulating effects. Test-tube studies have shown that lingzhi can boost the immune system by increasing the activity of white blood cells.
Mushrooms and Thrush: Is There a Connection?
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Lingzhi is rare in its natural form but can be cultivated on hardwood logs, sawdust, or woodchips
Lingzhi, also known as reishi, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in Asia. It has been recognised as a medicinal mushroom for over 2,000 years, with some evidence suggesting its use in Neolithic China 6,800 years ago. In nature, it grows at the base and stumps of deciduous trees, especially maples. However, it is extremely rare in its natural form, with only two or three out of 10,000 such trees exhibiting lingzhi growth.
Despite its rarity in the wild, lingzhi can be effectively cultivated on hardwood logs, sawdust, or woodchips. This cultivation method has made lingzhi readily available, and it is now used in traditional Chinese medicine and sold in shops. The process of cultivating lingzhi involves the development of a bracket that emerges from the log, which is the reproductive structure of the mushroom. This structure is called a mycelium, and it can live for decades.
The name "lingzhi" comes from Chinese, meaning "divine mushroom" or the "mushroom of immortality." It is regarded as the "herb of spiritual potency," symbolising success, well-being, divine power, and longevity. In Japan, the name for the Ganodermataceae family is "reishi" or "mannentake," meaning "10,000-year mushroom."
While the health benefits of lingzhi are largely based on anecdotal evidence and cultural mores, it is believed to have pharmaceutical properties, including the ability to control blood glucose levels, modulate the immune system, provide hepatoprotection, and exhibit bacteriostasis. Recent studies in the West have supported these claims, showing that lingzhi can stimulate the body's immune system and may help manage the function of T lymphocyte cells (T cells), which are critical parts of the immune system.
There is ongoing debate over the scientific name of the lingzhi mushroom, with some sources suggesting Ganoderma sichuanense as the accepted name, while others argue for Ganoderma lingzhi. This dispute arises due to the heavy dispute among mycologists regarding the taxonomy and nomenclature of the Chinese medicinal Ganoderma species.
Mushrooms in Fajitas: A Culinary Mystery Solved
You may want to see also

Its name means mushroom of immortality in Chinese
The lingzhi mushroom, also known as reishi, is a fungus that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. Its scientific name is Ganoderma lucidum, but it is often simply referred to as "lingzhi" or "reishi" in the East. The name "lingzhi" translates to "herb of spiritual potency," and it is considered a symbol of health, longevity, and divine power. In Chinese, its name means "mushroom of immortality," reflecting its historical reputation for promoting longevity and its use as a tonic for overall health and vitality.
The lingzhi mushroom is easily recognizable due to its unique appearance. It has a red, varnish-like sheen and a kidney-shaped cap with a woody texture. It is often depicted in Eastern art and symbolism, reflecting its cultural and medicinal significance. The mushroom grows on decaying logs and tree stumps, and while it is difficult to find in the wild, it can be cultivated artificially.
The belief in the lingzhi mushroom's ability to confer immortality is deeply rooted in Chinese folklore and traditional medicine practices. It is considered a superior herb in the East, reserved for emperors and royalty, who consumed it to promote longevity and enhance their spiritual power. The mushroom's rarity and distinctive appearance further added to its mystique and perceived value.
The lingzhi mushroom is believed to possess a range of medicinal properties, and its use is supported by both traditional knowledge and modern scientific research. It is often consumed as a tea or tincture, or in powdered or capsule form. Contemporary studies have suggested potential benefits of lingzhi mushroom extract, including immune-boosting, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
In traditional Chinese medicine, the lingzhi mushroom is classified as an adaptogen, meaning it helps the body adapt to stress and promotes homeostasis. It is believed to tonify the qi (life force energy) and support the immune system, making it a valuable tool for preventing illness and maintaining overall health. The lingzhi mushroom is also used to support liver health and promote calmness and restful sleep.
Overall, the lingzhi mushroom is a revered and respected symbol in Chinese culture and traditional medicine, earning its name as the "mushroom of immortality" through its historical use and perceived health benefits. Its medicinal properties continue to be explored and validated through scientific research, bridging the ancient wisdom of the East with modern wellness practices.
Mushrooms: A Natural Remedy for Bloating?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Lingzhi mushroom, also known as Ganoderma lucidum, is a fungus that grows in various hot and humid locations in Asia. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for over 2000 years.
The name Lingzhi comes from Chinese and means "divine mushroom" or the "mushroom of immortality". It symbolizes success, well-being, divine power, and
The Lingzhi mushroom is believed to have various health benefits, including boosting the immune system, controlling blood glucose levels, and hepatoprotection. It is also thought to have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antiulcer properties.
In nature, the Lingzhi mushroom grows at the base and stumps of deciduous trees, especially maples. It is rare in its wild form, with only 2 or 3 out of 10,000 such trees having Lingzhi growth. It can also be cultivated on hardwood logs, sawdust, or woodchips.
The Lingzhi mushroom is a large, dark mushroom with a glossy exterior and a woody texture. It usually has a flat, zoned structure with a reddish-brown, shiny top.











































