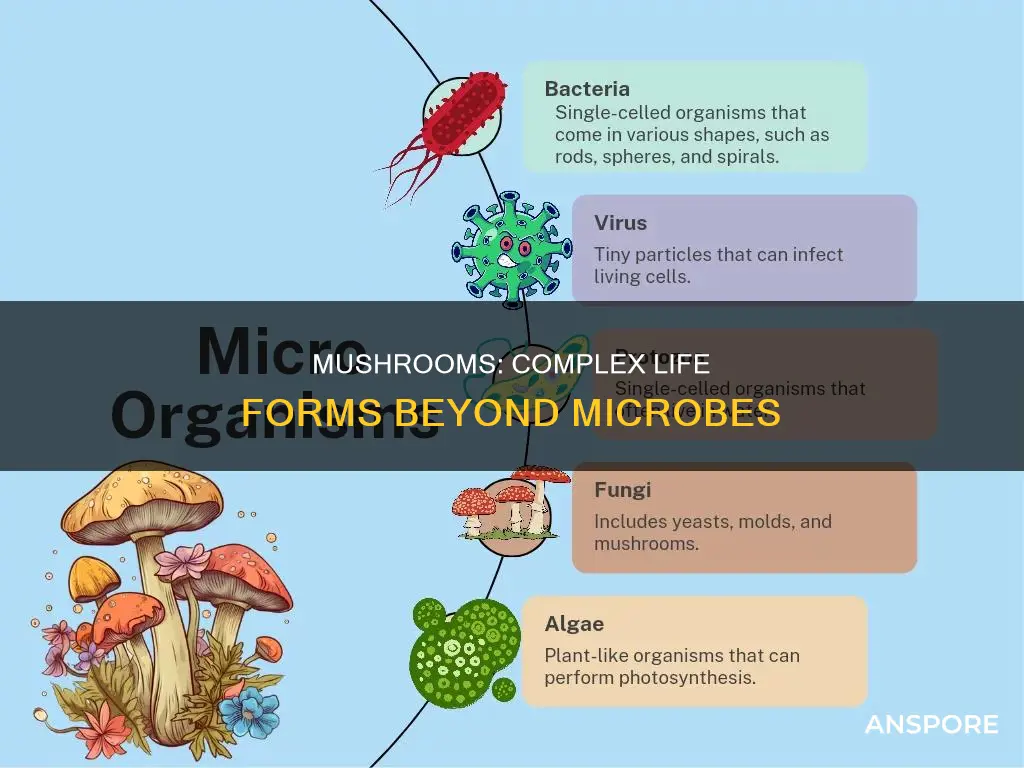
Mushrooms are the most well-known type of fungus, which are microorganisms that include yeasts and molds. Fungi are distinct from plants as they are more closely related to animals than plants. Fungi are classified as eukaryotes, which means they have cells, while microbes such as viruses and bacteria are smaller and less complex. Fungi are heterotrophs, acquiring food by absorbing dissolved molecules and secreting digestive enzymes, whereas microbes can be pathogenic, causing diseases such as COVID-19 and meningitis.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Mobility | Fungi are not immobile, unlike microbes |
| Cell Walls | Fungi have rigid cell walls that support them, unlike microbes |
| Chloroplasts | Fungi lack chloroplasts, unlike plants |
| Kingdom | Fungi are classified as a part of the kingdom Eumycota, separate from microbes |
| Food | Fungi acquire food by absorbing dissolved molecules, unlike microbes |
| Photosynthesis | Fungi do not photosynthesize, unlike plants |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn
- Mushrooms are fungi, which are more closely related to animals than plants
- Fungi are eukaryotes, meaning they have cells, unlike microbes
- Fungi are immobile, whereas microbes can travel through the air or water
- Fungi do not photosynthesize, unlike some microbes
- Mushrooms form through a mutual relationship with plants, which is not true for microbes

Mushrooms are fungi, which are more closely related to animals than plants
Mushrooms are a type of fungus, and fungi form a distinct kingdom of organisms separate from plants, bacteria, and some protists. Fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. This is because, initially, there was a common ancestor between plants, animals, and fungi. However, over time, the common ancestor of plants diverged from the common ancestor of animals and fungi. Subsequently, animals and fungi also separated, but this occurred much later in evolutionary history, indicating a closer relationship between the two.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms, meaning they have membrane-bound organelles and structurally complex cells. They are also heterotrophs, meaning they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules from their environment. This is in contrast to plants, which photosynthesize to produce their food. The presence of chitin in their cell walls is another characteristic that distinguishes fungi from plants.
The study of fungi is known as mycology, which was historically considered a branch of botany, reflecting the belief that fungi were primitive plants. However, recent advances in genetics and molecular biology have revealed that fungi are genetically more closely related to animals than to plants. This is supported by molecular phylogenetics, which demonstrates that fungi and animals share a more recent common ancestor than either group does with plants.
While mushrooms may visually resemble plants, particularly when they fruit, they are fundamentally different. Mushrooms are the fruiting bodies of macroscopic filamentous fungi. Their texture can sometimes feel similar to meat, further highlighting their distinctness from plants. Genetic studies provide strong evidence for the close relationship between animals and fungi, with some research even suggesting that animals and fungi are each other's closest relatives.
Best Way to Dry Mushrooms Using an Oven
You may want to see also

Fungi are eukaryotes, meaning they have cells, unlike microbes
Fungi, including mushrooms, are classified as eukaryotes, which means they have cells. This distinguishes them from microbes, which are typically prokaryotic and lack membrane-bound organelles. Fungi are more closely related genetically to animals than to plants, and they share characteristics with animals, such as heterotrophy, or the ability to acquire food by absorbing dissolved molecules.
Fungi, including mushrooms, have rigid cell walls that support them and contain chitin, a characteristic that differentiates them from plants, bacteria, and some protists. Fungi do not photosynthesize and are not immobile, as early taxonomists believed. Instead, they grow and spread through spores, which can travel through the air or water. Some spores are flagellated, allowing for additional mobility.
Mushrooms, as representatives of the fungus kingdom, play a significant role in human societies. They are a source of food, medicinal compounds, and mycelium materials. Mushrooms also establish mutualistic relationships with plants, aiding in the degradation of organic waste.
While most microbes are harmless, some are pathogens and can cause diseases in humans, such as pneumonia and COVID-19. Fungi can also be responsible for infections, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems. Examples of fungal infections include yeast infections, valley fever, and meningitis.
In summary, mushrooms are not considered microbes because they belong to the kingdom of fungi, which are eukaryotic organisms with cells. Fungi share similarities with both plants and animals but are genetically more closely related to animals. Their unique characteristics, such as cell walls containing chitin and their ability to spread through spores, distinguish them from microbes.
Blue Mushrooms: Potency and Power
You may want to see also

Fungi are immobile, whereas microbes can travel through the air or water
Fungi, including mushrooms, are immobile. This was one of the characteristics observed by early taxonomists that led to the classification of fungi as distinct from animals. However, it is important to note that fungi are not entirely immobile. While the fungi themselves do not move, their spores can travel through the air or water.
In contrast, microbes can move through the air or water and can be spread over long distances. Microbes include bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. Bacteria are larger and more complex than viruses but can still spread through the air. They can live and reproduce almost anywhere, including in the soil, water, and even in our bodies.
Viruses, on the other hand, are much simpler in structure and cannot survive or replicate on their own. They need to enter a living organism to replicate and spread. While most microbes are harmless, some can be pathogenic and cause diseases such as pneumonia or COVID-19.
Fungi are more complex organisms than viruses and bacteria. They are eukaryotes, which means they have cells, and their structure is more similar to animals than to plants. Fungi acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules and secreting digestive enzymes, rather than through photosynthesis.
While mushrooms are a well-known type of fungus, most fungi are inconspicuous due to their small size and cryptic lifestyles in soil or on dead matter. Fungi can form mutualistic relationships with plants and play important roles in human societies, such as in medicine and as a food source.
Herbs and Mushrooms: Perfect Pairing Guide
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Fungi do not photosynthesize, unlike some microbes
Fungi, including mushrooms, are not microbes. Fungi are a distinct group of organisms, called the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes). They are classified as eukaryotic organisms, which include microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as mushrooms. Fungi are placed in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists due to the presence of chitin in their cell walls.
Fungi are heterotrophs, which means they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules. They do this by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Unlike plants, fungi do not photosynthesize. Instead, they use growth as their means of mobility, except for spores, which may travel through the air or water.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar. This process is carried out by chloroplasts, which contain the pigment chlorophyll. Fungi, however, lack chloroplasts, which is one of the reasons they cannot photosynthesize.
While fungi do not photosynthesize, they can form symbiotic relationships with photosynthetic organisms. Lichens, for example, are a combination of a fungus and a photosynthetic organism, usually an alga or cyanobacterium. In this relationship, the fungus provides minerals and water, while the photobiont (the photosynthetic partner) provides sugars and other carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis.
In summary, fungi, including mushrooms, are not classified as microbes. They are a distinct group of organisms with unique characteristics, including the absence of photosynthetic abilities. Instead, they acquire their energy by absorbing dissolved molecules from their surroundings.
Puffball Mushrooms: Black Transformation Explained
You may want to see also

Mushrooms form through a mutual relationship with plants, which is not true for microbes
Mushrooms are fungi, which are distinct from microbes such as bacteria and other microorganisms. Fungi are classified as eukaryotic organisms, a category that also includes plants and animals. However, fungi are genetically more closely related to animals than to plants. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs, acquiring food by absorbing dissolved molecules and secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. They do not photosynthesize.
Mushrooms form mutualistic and symbiotic relationships with plants through their mycelial networks. This relationship is known as mycorrhizal association, where mushrooms trade nutrients with plants for carbohydrates. This subterranean network facilitates the exchange of information and resources between different species across vast underground territories. In this way, mushrooms act as nature's internet, connecting disparate life forms through cooperative networks.
The relationship between mushrooms and plants is beneficial for both organisms. Plants provide sugars and energy, while mushrooms harvest the nutrients and trace minerals that plants need. This mutual dependence ensures the survival of both mushrooms and plants. Additionally, mushrooms can help colonize and restore depleted soils, remediate pollution, break down plastics, and contribute to curbing climate change.
In contrast, microbes do not form similar mutual relationships with plants. Instead, microbes like bacteria and fungi can exist in the soil, and their presence may be beneficial or harmful to plants. While some microbes can have positive impacts, such as endophytes contributing to the flavor of grapes, others can invade and cause problems for plants, such as foliar blight and root rot. Therefore, the presence of microbes in relation to plants is more complex and variable, lacking the consistent mutualism seen between mushrooms and plants.
Mushrooms and the Torah: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Mushrooms are not microbes because they are fungi, which are larger and more complex organisms. Fungi are eukaryotes, meaning they have cells, while microbes are typically used to refer to microscopic organisms like bacteria and viruses. Fungi are more closely related to animals than plants or microbes.
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can live and reproduce on their own, whereas mushrooms are formed by fungi, which are multicellular organisms. Bacteria can be beneficial or harmful to humans, while mushrooms can be a source of food, medicine, and other useful materials.
While mushrooms are not microbes, they can share similarities with certain microbes. For example, both fungi and bacteria can cause different types of infections in humans, such as pneumonia. Additionally, bacteria interact with mushroom-forming fungi and play a beneficial role in stimulating growth and protecting against other pathogens.











































