Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been shown to effectively treat depression and several other mental health conditions. However, there are concerns about its interaction with antidepressants, particularly the risk of serotonin toxicity. While some studies suggest that psilocybin's effects may be diminished when combined with certain antidepressants, others indicate a potential danger of serotonin toxicity, especially when used with other serotonergic medications. As public interest in microdosing psychedelics grows, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the potential risks and benefits of combining psilocybin with antidepressants.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Will mushrooms react with antidepressants? | Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, may cause serotonin toxicity when used with antidepressants. |
| What is serotonin toxicity? | Serotonin toxicity, or serotonin syndrome, occurs when there is a build-up of serotonin in the brain, which can lead to potentially life-threatening symptoms. |
| How do mushrooms interact with antidepressants? | Mushrooms contain psilocybin, which alters neurotransmitter systems in the brain and activates serotonergic receptors. This can cause a wave of unique excitatory activity in the brain, leading to cognitive effects such as ego-dissolution and alterations in the subjective experience of time. |
| What are the risks of combining mushrooms and antidepressants? | Combining mushrooms with certain antidepressants can lead to dangerous or undesirable interactions and may pose a risk of serotonin toxicity. |
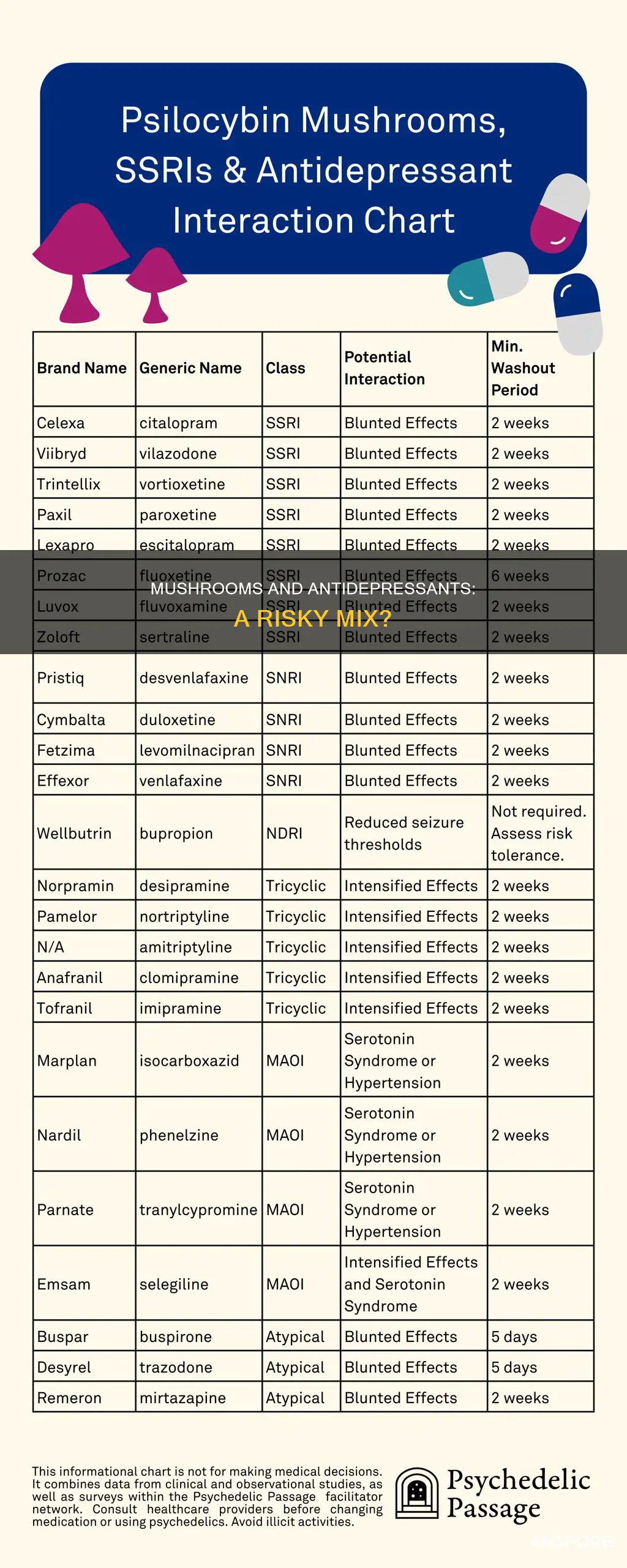
| Are there any known interactions between mushrooms and specific types of antidepressants? | SSRIs and SNRIs appear to weaken the effects of psilocybin-containing mushrooms. MAOIs, or Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors, can also affect serotonin levels in the brain and may have additional unintended effects when combined with psilocybin. Lithium, a mood-stabilizing drug, should not be ingested with psilocybin due to the risk of seizures. |
| Are there any benefits to combining mushrooms and antidepressants? | Some studies suggest that psilocybin can effectively treat depression and improve symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It may also lead to heightened mental functioning and a better sense of well-being. |
| What should someone considering combining mushrooms and antidepressants do? | It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before combining any psychedelics with medications. Seeking advice from experienced medical and mental health practitioners can be helpful in the decision-making process. |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Serotonin toxicity
Serotonin syndrome is a drug reaction that occurs when certain drugs or medications that affect serotonin levels are taken. This includes prescription medications, over-the-counter drugs, herbal or dietary supplements, and illegal drugs. It is most often caused by combining medications that contain serotonin, such as a migraine medication and an antidepressant. It can also occur when there is an increase in the dosage of a drug that increases serotonin levels.
The symptoms of serotonin syndrome can range from mild to severe and can include shivering, diarrhoea, nausea, high fever, seizures, muscle rigidity, and confusion. Severe serotonin syndrome can be fatal if not treated quickly.
A case study has highlighted the danger of serotonin toxicity when psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, is used alongside antidepressants. Psilocybin has attracted attention for its potential to treat symptoms of major depressive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. However, as it works through the serotonergic system, combining it with certain medications can lead to a risk of serotonin toxicity. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a healthcare provider before mixing any psychedelics with medications.
Magic Mushroom Spores: Legal or Not?
You may want to see also

Psilocybin and antidepressants
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been the subject of numerous studies investigating its potential to treat major depressive disorder (MDD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While psilocybin has demonstrated antidepressant properties, there are concerns about its interaction with other medications, particularly antidepressants.
The concurrent use of psilocybin and antidepressants has been associated with serotonin toxicity, also known as serotonin syndrome. Serotonin toxicity occurs when there is an excessive buildup of serotonin in the brain, leading to potentially life-threatening symptoms. Although psilocybin is generally considered safe when used alone, combining it with other medications can pose risks.
A case study published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry highlighted this risk. The patient, a 35-year-old woman with a history of MDD, chronic PTSD, and generalized anxiety disorder, was taking a daily regimen of antidepressants and had recently started using psilocybin recreationally. The authors suggested that the patient's unregulated use of psilocybin in conjunction with her medication regimen may have contributed to her heightened risk of serotonin toxicity.
Limited data suggest that psilocybin's effects may be diminished when used with serotonergic antidepressants, both acutely and after a medication washout period. This has been supported by reports of individuals taking mushrooms with antidepressants, where the probability of weaker-than-expected drug effects was higher with the concurrent use of selective serotonergic reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs).
However, it is important to note that the interaction between psilocybin and SSRIs is still being studied. While some research suggests that SSRIs may weaken the effects of psilocybin, an open-label trial found that a single administration of psilocybin with psychological support adjunctive to SSRI demonstrated favourable safety and therapeutic efficacy in patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Additionally, a double-blind randomized controlled trial found that SSRI administration for 2 weeks did not significantly alter the acute subjective effects of 25 mg of psilocybin.
In conclusion, while psilocybin has shown promise in treating mood disorders, caution must be exercised when combining it with antidepressants due to the risk of serotonin toxicity. More research is needed to fully understand the interaction between psilocybin and specific types of antidepressants, such as SSRIs and SNRIs. Individuals taking antidepress medications should always consult with their healthcare provider before considering the use of psilocybin.
Mushrooms: The Surprising Cause of Flatulence?
You may want to see also

Safety concerns
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been shown to be effective in treating depression and other mental health conditions. However, there are safety concerns when it comes to combining psilocybin with antidepressant medications.
One of the main concerns is serotonin toxicity, also known as serotonin syndrome. Serotonin toxicity occurs when there is an excessive amount of serotonin in the brain, which can lead to potentially life-threatening symptoms. As psilocybin activates serotonergic receptors in the brain, combining it with other serotonergic medications, such as SSRIs or SNRIs, can increase the risk of serotonin toxicity. A case study reported in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry highlighted this risk, demonstrating that unregulated psilocybin use alongside other medications can pose serious risks.
Another concern is the potential for adverse interactions between psilocybin and certain antidepressants. While research is still ongoing, limited data suggest that psilocybin's effects may be diminished by serotonergic antidepressants, even after a medication washout period. This means that combining psilocybin with certain antidepressants may reduce the effectiveness of the mushroom. Additionally, some antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants, are known for their serious side effects, and combining them with psilocybin may pose a risk for serotonin syndrome, although this risk is considered low.
It is also important to note that lithium, a mood-stabilizing drug sometimes used for depression, should not be ingested with psilocybin. Combining lithium with psilocybin has been associated with a significant possibility of seizures.
Furthermore, as the use of psilocybin in therapeutic settings increases, it is crucial to recognize that future treatment demands careful monitoring, especially when patients are using other serotonergic agents concurrently. While some sources suggest that psilocybin is generally safe when combined with most antidepressants, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before mixing any psychedelic with prescription medication.
Mushrooms: Nature's Heterotrophs
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Therapeutic effects
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been shown to be effective in treating depression and other mental health conditions. However, there are concerns about potential negative interactions when combining psilocybin with certain antidepressants.
Psilocybin has attracted attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic benefits, particularly in the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is known for producing unique cognitive effects, including ego-dissolution, changes in external perception, and alterations in the subjective experience of time.
One notable therapeutic effect of psilocybin is its ability to "reset" brain circuits in individuals with depression. This reset enhances emotional receptivity, which is the opposite of how selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants work. By increasing emotional receptivity, psilocybin allows individuals to accept and process a wider range of emotions, including negative ones, leading to improved clinical outcomes.
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans have provided valuable insights into psilocybin's therapeutic effects. These scans have shown heightened activity in the right amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotional reactions. Specifically, psilocybin increased responses to both fearful and happy faces, with the increases in response to fearful faces being predictive of clinical improvements in depressive symptoms.
The therapeutic benefits of psilocybin are particularly notable in cases of treatment-resistant depression. In a study of 20 patients with moderate-to-severe treatment-resistant depression, psilocybin produced positive effects on brain activity and depressive symptoms. These effects were found to last longer than typical treatments, especially when combined with skilled therapeutic integration programs.
While the exact mechanisms are not yet fully understood, psilocybin's ability to alter neurotransmitter systems in the brain and activate serotonergic receptors is believed to play a key role in its therapeutic effects. This activation of serotonergic receptors causes a wave of unique excitatory activity throughout the main perceptual centers of the mind, leading to significant cognitive and emotional shifts.
In addition to its therapeutic benefits for depression, psilocybin has also been associated with persisting improvements in overall mental health and well-being. Some individuals who have combined psilocybin with antidepressants have reported heightened mental functioning and a better sense of well-being. However, it is important to note that the safety and long-term effects of combining psilocybin with antidepressants are still under review, and there are concerns about potential serotonin toxicity.
Mushrooms: How Do They Feed?
You may want to see also

Clinical studies
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been the subject of numerous clinical studies in recent years for its potential in treating symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While psilocybin has shown promise in treating mood disorders, it also carries risks when used in conjunction with other drugs, particularly antidepressants.
One case study highlighted the danger of serotonin toxicity when psilocybin is used alongside antidepressants. Serotonin toxicity, also known as serotonin syndrome, occurs when an excessive amount of serotonin builds up in the brain, leading to potentially life-threatening symptoms. This risk is heightened when psilocybin is combined with other serotonergic medications, as both substances work on increasing serotonin levels in the brain.
Several clinical studies have investigated the effects of combining psilocybin with antidepressants. One study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, compared the effects of psilocybin and escitalopram, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), in a randomized controlled trial involving patients with long-standing, moderate-to-severe major depressive disorder. The trial found that psilocybin may have antidepressant properties, but direct comparisons with established treatments like escitalopram are lacking.
Another study, published in PubMed, examined the attenuation of psilocybin mushroom effects during and after SSRI/SNRI antidepressant use. The study analyzed reports from individuals who took mushrooms with an antidepressant and found that the probability of weaker than expected drug effects was higher when psilocybin was combined with SSRIs or SNRIs. This suggests that SSRIs and SNRIs may diminish the effects of psilocybin-containing mushrooms.
While there are no reports of serious adverse effects from combining psilocybin with SSRIs or SNRIs, it is important to note that the combination may reduce the effectiveness of psilocybin. Additionally, the risk of serotonin syndrome remains a concern, especially for individuals who increase their intake of magic mushrooms due to initially low effects. As such, it is recommended to consult a healthcare provider before mixing any psychedelic with medications.
Mushroom Risotto: Perfect Pairing Ideas for a Hearty Dish
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Psilocybin, a psychedelic compound found in some mushrooms, has been shown to be effective in treating depression. However, when combined with certain antidepressants, there is a risk of serotonin toxicity, also known as serotonin syndrome, which can be life-threatening.
Combining mushrooms with certain antidepressants can lead to weakened or blunted effects of the mushrooms. This may be due to the antidepressants diminishing the effects of psilocybin. Additionally, there is a risk of overstimulating the body if psilocybin is combined with medications that work on the serotonergic system.
It is generally not recommended to combine mushrooms with antidepressants without medical supervision. While some studies suggest that psilocybin is safe to combine with most antidepressants, there are specific medications that can have dangerous or undesirable interactions. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional before mixing any psychedelics with medications.











































