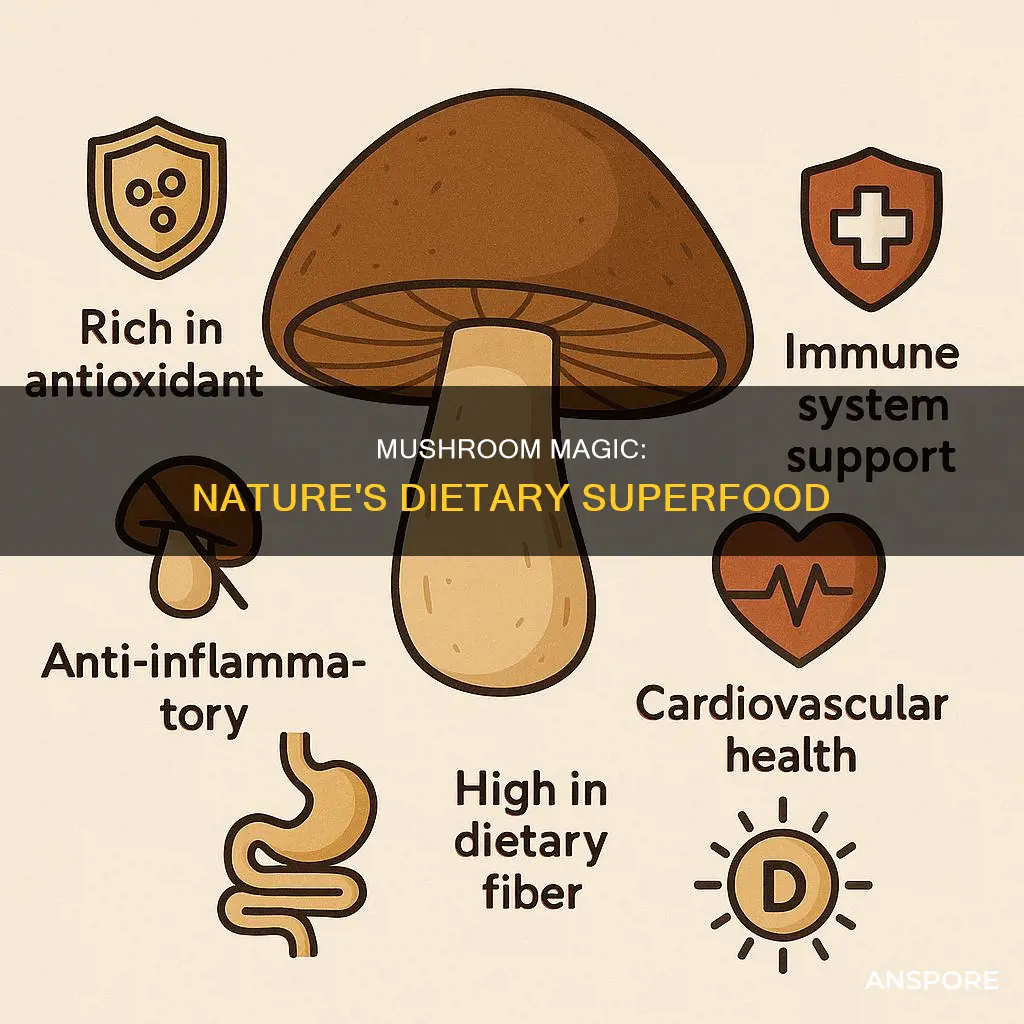
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that has been consumed and used as medicine for thousands of years. They are a rich source of potassium, vitamin C, vitamin D, and dietary fiber. They are also low in calories, fat, and sodium, making them a healthy addition to any diet. Mushrooms have been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects, and may help to prevent various health conditions such as Alzheimer's, heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. With their delicate flavor and meaty texture, mushrooms are a versatile ingredient in many dishes and can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Fungi |
| Number of Species | Over 1 million |
| Number of Edible Varieties | Over 2,000 |
| Common Varieties | Cremini, Truffles, Button, Portobello, Shiitake, Porcini, Chanterelle, Maitake, Enoki, Morel, Oyster |
| Vitamins | B6, D, E, K, C, B12 |
| Minerals | Zinc, Potassium |
| Other Nutrients | Fiber, Protein, Antioxidants, Polyphenols, Ergothioneine, Selenium, Choline |
| Health Benefits | May help prevent cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer's, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease |
| Culinary Use | Can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked; used as a substitute for meat |
| Sustainability | Produced in 33 states in the US; family-owned farms; recycling byproducts from other agricultural sectors |
| Consumption | Average American eats approximately 3 pounds of mushrooms per year |
Explore related products
What You'll Learn

Mushrooms are a source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that contains a substance called ergosterol, which is similar in structure to cholesterol in animals. When exposed to ultraviolet light, ergosterol transforms into vitamin D, an important component for bone and immune health. Mushrooms are a good source of vitamin D, with estimates showing that fresh wild mushrooms like chanterelles and morels can contain up to 1200 IU per 3.5-ounce serving. Vitamin D helps with cell growth and has been linked to a reduced risk of certain types of cancer.
In addition to vitamin D, mushrooms also contain selenium, vitamin B6, and other B vitamins. Selenium can help prevent cell damage, while vitamin B6 helps our bodies form red blood cells. Mushrooms are also a rich source of potassium, which is known for reducing the negative impact of sodium on the body and lessening tension in blood vessels, thereby helping to regulate blood pressure. The potassium, vitamin C, and fiber in mushrooms contribute to cardiovascular health and may help lower the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
Mushrooms also contain various antioxidants, which may help to prevent several health conditions such as cancer and diabetes when consumed as part of a nutritionally balanced diet. Choline, an antioxidant found in mushrooms, has been studied for its potential in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory effects of mushrooms have been shown to improve the efficiency of the immune system. Plant chemicals and components in mushrooms, such as polysaccharides, indoles, polyphenols, and carotenoids, have been found to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects in cell and animal studies.
Mushrooms are also a good source of protein and fiber, making them a nutritious addition to any diet. They are low in calories and fat, making them a healthy option for weight management. Furthermore, mushrooms contain an amino acid called glutamate, which gives them a savory rich flavor known as umami. This makes mushrooms a tasty and versatile ingredient that can enhance the flavor of many dishes.
How Mushrooms Boost Ailanthone's Power
You may want to see also

They are low in calories, fat, and sodium
Mushrooms are a type of fungus that has been consumed and used as medicine for thousands of years. They are a good source of antioxidants and vitamins and are known for their delicate flavour and meaty texture. They are also low in calories, fat, and sodium, making them a healthy and tasty addition to any diet.
Mushrooms are a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes. They can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked, and they provide a variety of flavours and textures. Mushrooms are also known for their umami taste, which is a savoury, rich flavour that comes from the amino acid glutamate. This makes mushrooms an excellent substitute for meat in many dishes, especially red meat, as they can help to minimise calories, fat, and cholesterol intake.
The low sodium content of mushrooms is particularly noteworthy. A cup of white button mushrooms, for example, contains just five milligrams of sodium. This makes mushrooms a great ingredient for reducing sodium intake and maintaining healthy blood pressure. In fact, a study from the Culinary Institute of America and UC Davis found that swapping half the meat for mushrooms in a traditional ground beef recipe reduced sodium intake by 25% without compromising flavour.
The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends reducing salt intake and increasing consumption of foods containing potassium, and mushrooms fit the bill perfectly. They are a good source of potassium, which can help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
In addition to being low in calories, fat, and sodium, mushrooms also have unique nutritional benefits. They are one of the few plant-based sources of vitamin D, which is important for bone health and immune function. Mushrooms also contain ergothioneine, an amino acid and antioxidant that prevents or slows cellular damage. Overall, mushrooms are a nutritious and delicious addition to any meal, offering a variety of health benefits.
Evolution of Tiny Mushrooms: From Spores to Caps
You may want to see also

Mushrooms may help prevent cancer and other serious health conditions
Mushrooms have been used as food and medicine for thousands of years. They are a type of fungus, and there are over 10,000 known types. They are low in calories and fat and contain various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Mushrooms have been linked to a reduced risk of several serious health conditions, including cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer's, and diabetes. Some studies have shown that cancer patients who consume mushrooms may live longer. This may be due to the positive impact on their immune response, allowing them to tolerate more rounds of chemotherapy treatment. Mushrooms are also said to improve several quality-of-life indicators for cancer patients, including appetite, physical and mental competency, and reduced fatigue.
Mushrooms are rich in antioxidants, which may help protect against oxidative stress and lower the risk of cancer. They also contain vitamin D, which is essential for immune health. However, the amount of vitamin D in mushrooms varies depending on their exposure to UV light. Wild mushrooms like chanterelles and morels can contain up to 1200 IU of vitamin D per 3.5-ounce serving, while those grown in dark conditions contain much less.
Mushrooms also contain potassium, which can help regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, their anti-inflammatory properties can improve immune system efficiency.
While the health benefits of mushrooms are promising, more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness in preventing and treating various health conditions. Most studies on mushrooms and cancer have been conducted in Asia, and it is unclear if the results can be generalized to other populations.
How Mushroom Clouds Form and Why
You may want to see also
Explore related products

They are a good substitute for meat
Dietary mushrooms are a unique type of fungus that have long been recognized for their nutritional and medicinal properties. They are distinct from the typical button mushrooms found in grocery stores, offering a range of potential health benefits. One of their most notable attributes is their ability to serve as a nutritious and tasty substitute for meat.
Meat has traditionally been a significant source of protein and other essential nutrients in the human diet. However, in recent times, with a growing awareness of the environmental impact of meat production and concerns about animal welfare, many people are exploring alternative sources of protein. This is where dietary mushrooms step in as a versatile and healthy meat alternative.
Mushrooms, in general, are a good source of protein, and dietary mushrooms are no exception. While they may not contain as much protein as meat, they still offer a considerable amount. For instance, a 100-gram serving of portabella mushrooms provides about 3 grams of protein, which is comparable to the protein content in a similar serving of ground beef.
Additionally, dietary mushrooms are a rich source of B vitamins, including riboflavin, niacin, and pantothenic acid, which are essential for energy production and overall health. They also contain minerals like selenium, potassium, and phosphorus, which are often found in meat. By including a variety of dietary mushrooms in your meals, you can ensure that you're getting a good balance of these important nutrients.
The texture of cooked mushrooms is also similar to meat, especially when they are prepared in certain ways. For instance, portabella mushrooms have a meaty texture and a savory taste, making them a popular choice for vegetarian burgers and sandwiches. Their ability to absorb flavors from marinades and spices also makes them extremely versatile in various recipes. With their dense and chewy texture, they can satisfy the craving for a hearty, meaty meal without the need for animal-based products.
So, whether you're looking to reduce your meat consumption for health, environmental, or ethical reasons, dietary mushrooms present a tasty and nutritious option. They can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes, adding not only nutritional value but also a satisfying texture and flavor that will leave you feeling content and nourished.
Mushroom Cultivation: Edible Fungi Farming Techniques
You may want to see also

Mushrooms are a type of fungus
Edible mushrooms can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked. The most common type is the button mushroom, but there are many other varieties such as portobello, shiitake, porcini, chanterelle, maitake, enoki, morel, cremini, and oyster mushrooms. They are a versatile ingredient in many cooking styles, as they provide a variety of flavours and textures. Wild mushrooms can be dangerous, as some contain deadly toxins, high levels of heavy metals, and other harmful chemicals. Therefore, it is important to only consume mushrooms from a reliable source.
Mushrooms are low in calories, fat, and sodium, and contain modest amounts of fibre, protein, and various nutrients, including vitamins B6, C, and D, potassium, and choline. They also contain non-nutritive substances such as polysaccharides, indoles, polyphenols, and carotenoids, which have been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects. The antioxidant ergothioneine, for example, prevents or slows cellular damage. The anti-inflammatory effects of mushrooms have also been shown to improve the efficiency of the immune system.
Mushrooms are the only type of produce that is a source of vitamin D, which helps the body absorb calcium for strong bones. Vitamin D is produced when mushrooms are exposed to UV light or sunlight. They are also a good source of potassium, which helps to regulate blood pressure and maintain heart health. Additionally, mushrooms can be used as a substitute for meat in many dishes, helping to reduce cholesterol levels and lower blood pressure.
Mushroom Freezing: Do Nutrients Survive the Deep Freeze?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Dietary mushrooms are a type of fungus that contains a substance called ergosterol, which is similar to cholesterol in animals. Mushrooms are low in calories and fat, and contain modest amounts of fibre, protein, and various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Mushrooms are a source of vitamin D, B6, and K, potassium, selenium, choline, zinc, and fibre.
Mushrooms are associated with a reduced risk of several serious health conditions, including certain types of cancer, heart disease, Alzheimer's, and type 2 diabetes. They may also help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
There are over 10,000 known types of mushrooms, with more than 2,000 edible varieties. Common edible mushrooms include button, portobello, cremini, shiitake, porcini, chanterelle, maitake, enoki, morel, and oyster mushrooms.
Mushrooms can be eaten raw, dried, or cooked. They can be sautéed in olive oil, simmered in water, or sprinkled raw over meals. Dried mushrooms should be soaked in water for several hours until soft.











































