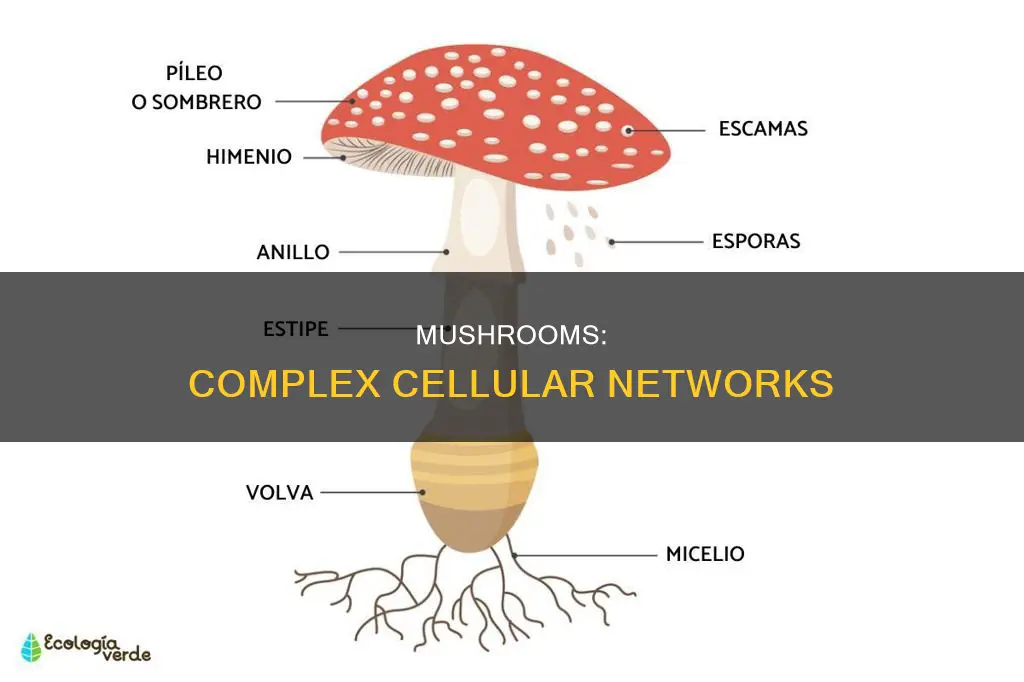
Mushrooms are a type of fungus, which are eukaryotic multicellular organisms. Fungi are distinct from plants and animals, having diverged from them around one billion years ago. Fungi have membrane-bound nuclei with chromosomes that contain DNA, and their cells are long and thread-like, connected end-to-end. These cells, called hyphae, form a network called a mycelium, which makes up most of the body of a fungus. Mushrooms are the fruiting bodies of fungi, used to store and
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cell structure | Long and thread-like filaments called hyphae, connected end-to-end |
| Cell wall composition | Chitin, a derivative of glucosamine, unique to fungi |
| Multicellular | Yes, but some species are single-celled |
| Cell nuclei | Multiple nuclei per cell |
| Eukaryotic | Yes |
| Autotrophs | No, they are heterotrophs |
| Nitrogen fixation | No, they must obtain nitrogen from their diet |
| Digestion | External, through exoenzymes |
| Polysaccharide storage | Glycogen |
| Ecological role | Decomposers of dead plant material, recycling nutrients |
| Uses | Food, fermentation, antibiotics, pesticides, bioremediation |
Explore related products
$11.99
What You'll Learn
- Mushrooms are a type of fungus, which are multicellular organisms
- Fungi cells are long and thread-like, connected end-to-end
- Fungi cell walls are made from chitin, a compound not found in plants
- Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they consume other life to get energy
- Fungi are used in food preparation, medicine, and industrial production

Mushrooms are a type of fungus, which are multicellular organisms
Fungi are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. They are heterotrophs, which means they must consume other organisms to obtain energy, similar to animals. Fungi do not photosynthesise like plants, instead, they absorb nutrients from their environment through osmosis. This is achieved via a network of long, thin filaments called hyphae, which are connected end-to-end and comprise the body of the fungus. Each hypha is a single cell, and they can contain multiple nuclei. When woven together, they form a mycelium, which is the living, growing portion of the fungus. Mycelia provide a large surface area, making fungi well-adapted to absorbing nutrients from their surroundings.
The fruit bodies of some fungi are known as mushrooms. These are the reproductive organs of the fungi and are used to store and release spores. Mushrooms are usually conspicuous and can sometimes resemble plants. They come in a variety of colours, with pigments associated with their cell walls, which play a protective role against ultraviolet radiation and can be toxic.
Fungi have a diverse range of uses and are important decomposers of dead plant material, recycling nutrients back into ecosystems. They are used as a food source, in fermentation, and in the production of antibiotics. Fungi also have industrial applications, such as in the production of enzymes and biological pesticides.
Mushroom Storage: Fridge or No Fridge?
You may want to see also

Fungi cells are long and thread-like, connected end-to-end
Fungi are a kingdom of mostly microscopic organisms. They are neither plants nor animals, but form a separate kingdom of their own. Fungi are eukaryotic multicellular organisms, composed of filaments called hyphae. These hyphae are long, thin, and tubular cells that are connected end-to-end. Each cell is surrounded by a unique cell wall composed of a compound called chitin, which is also found in the exoskeletons of arthropods such as insects and crustaceans.
Chitin is a tough molecule that forms long chains and meshes, providing a 3D skeleton and structural strength to the fungal cells. The presence of chitin in cell walls is a defining feature of the fungi kingdom, distinguishing them from plants, bacteria, and some protists, which have cell walls made from other compounds like cellulose.
The network of hyphae in a fungus is called a mycelium, and it can be very large, providing a huge surface area for the fungus. This large surface area is advantageous for absorbing nutrients from the surrounding soil or other substrates. The mycelium secretes digestive enzymes and slowly consumes the resulting nutrients through osmosis, breaking down insoluble polysaccharides like cellulose and lignin into absorbable glucose molecules.
Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they must consume other life forms to obtain energy, similar to animals. They are mostly saprobes, deriving their nutrients from decaying organic matter, particularly dead plant material. Fungi play a crucial role in ecosystems by decomposing dead plants and recycling nutrients back into the environment, ensuring habitats remain fertile and capable of supporting life.
Mushrooms: Cancer-Fighting Superfood?
You may want to see also

Fungi cell walls are made from chitin, a compound not found in plants
Fungi, including mushrooms, are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals. They have unique features and traits, including specialized cell walls.
Chitin is more resistant to degradation by enzymes and other organisms, protecting fungal cells from external threats. It also facilitates tighter junctions between cells, maintaining the integrity of the cell wall and preventing the entry of harmful substances. Additionally, chitin is beneficial for nutrient absorption and transportation within fungal cells, allowing them to efficiently obtain and utilize nutrients from their surroundings.
In contrast to fungi, plant cell walls are made of cellulose, which is produced through photosynthesis and provides structure to plant-derived products like wood and paper. Fungi, lacking chloroplasts, do not undergo photosynthesis and are typically found in poorly lit or dark places. As a result, they have adapted to have chitin in their cell walls instead of cellulose.
Medicinal Mushrooms: Nature's Superpowers Explained
You may want to see also
Explore related products

Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they consume other life to get energy
Mushrooms are a type of fungus, which are now considered a separate kingdom, distinct from both plants and animals. Fungi have membrane-bound nuclei with chromosomes that contain DNA. They also have distinct cell walls, which contain chitin, a derivative of glucosamine. This substance is not found in plants, but it is found in the exoskeletons of arthropods, such as insects and crustaceans.
Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they cannot produce their own food and must consume other life to obtain energy. They are similar to animals in this respect, as they absorb nutrients from their environment. This is in contrast to autotrophs, which can produce their own organic matter using inorganic sources of carbon and energy. Autotrophs include plants, which use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into organic carbon compounds.
Heterotrophs are vital parts of Earth's biogeochemical cycles, particularly in the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles. They obtain energy and carbon by consuming organic matter, which is made up of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. These organic compounds are oxidised, releasing energy that is stored as ATP, the 'energy currency' of cells.
Fungi, as heterotrophs, play a key role in the carbon cycle, acting as both consumers and decomposers. They release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere through respiration, making carbon available for autotrophs to fix through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. This circulation supports the continuous cycling of carbon between organic and inorganic forms.
The Magic of Mushroom Mass Production
You may want to see also

Fungi are used in food preparation, medicine, and industrial production
Fungi have been used in food preparation, medicine, and industrial production for thousands of years. They are a diverse group of organisms with a wide range of biological activities and chemical compounds that have proven useful in numerous applications.
Food Preparation
Fungi are used in the production of various foods, including bread, cheese, tofu, soy sauce, and flavour enhancers. In bread-making, fungi are used to leaven dough, aiding in the rising process and adding flavour. In cheese-making, certain species of fungi, such as Penicillium, are used to create popular cheeses like Camembert and Roquefort, also known as blue cheese. These "mold-ripened" cheeses rely on the addition of microorganisms in their manufacturing process, resulting in a magical transformation of milk into cheese. Tempeh, a food product made from fermented legume seeds with Rhizopus oligosporus, is another example of fungi in food preparation. The fungus is inoculated into boiled beans, digesting complex carbohydrates and other organic compounds, making it easier to digest and enhancing its flavour.
Medicine
Fungi have been used as medicines for centuries, playing a significant role in treating microbial infections. They are a source of antibiotics derived from penicillin, which have saved countless lives since the 1940s. These antibiotics have effectively treated bacterial infections such as meningitis, strep throat, whooping cough, tuberculosis, and pneumonia, as well as deadly infections from war wounds, dental procedures, and surgeries. Additionally, fungi from yeast have been used to combat bacterial infections, although they can also kill beneficial bacteria. Some people consume medicinal fungi in the form of pills or tinctures, believing that they can enhance their immune systems and prevent or treat various disorders, including diabetes, heart diseases, cancers, and Alzheimer's.
Industrial Production
Fungi are also employed in industrial applications, including the production of alternative fuels, pesticides, food, and vitamins. They are a significant source of pigments, enzymes, and other valuable chemicals. For example, endophytic fungi can degrade complex structures like lignocellulose, making them useful for producing fuel ethanol and other commodity chemicals. Additionally, they are being investigated for bioremediation purposes, such as cleaning up heavy metals, toxic wastes, radiation, and explosives. Fungi are also used in reforestation projects and have the potential to provide new, sustainable technologies that can replace synthetic substances.
Mushrooms: Nature's Decomposers and Their Role in the Ecosystem
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, mushrooms are made from a collection of fungal cells called 'hyphae'. These cells are long and thread-like and connected end-to-end.
Fungi are mostly microscopic organisms. They are eukaryotic multicellular organisms composed of filaments called hyphae. Each cell is surrounded by a cell wall made of a compound called chitin, which is unique to fungi.
Mushrooms are the fruiting body common to many species of fungi. They are used to store and











































